Làm Thế Nào Một Lò Phản Ứng Thủy Tinh Hóa Học Đạt Được Kiểm Soát Nhiệt Độ Chính Xác?
Giới Thiệu
Kiểm soát nhiệt độ là một trong những thông số quan trọng nhất trong các phản ứng hóa học. Ngay cả những dao động nhỏ cũng có thể ảnh hưởng đến tốc độ phản ứng, độ tinh khiết của sản phẩm, hiệu suất và độ an toàn. Điều này đặc biệt đúng trong R&D dược phẩm, tổng hợp hóa chất tốt và thử nghiệm ở quy mô phòng thí nghiệm.
Một lò phản ứng thủy tinh hóa học được thiết kế đặc biệt để cung cấp khả năng kiểm soát nhiệt độ ổn định, chính xác và có thể lặp lại. Trong bài viết này, chúng tôi giải thích làm thế nào lò phản ứng thủy tinh hóa học đạt được khả năng kiểm soát nhiệt độ chính xác, và tại sao khả năng này lại cần thiết cho quá trình xử lý hóa học hiện đại.
Tại Sao Kiểm Soát Nhiệt Độ Quan Trọng Trong Phản Ứng Hóa Học
Nhiều phản ứng hóa học rất nhạy cảm với sự thay đổi nhiệt độ. Kiểm soát nhiệt độ kém có thể dẫn đến:
Vì lý do này, các phòng thí nghiệm và nhà máy thí điểm yêu cầu các hệ thống lò phản ứng có thể duy trì nhiệt độ ổn định trong suốt quá trình phản ứng.
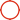
Vai Trò của Thiết Kế Áo Khoác
Cốt lõi của việc kiểm soát nhiệt độ chính xác trong lò phản ứng thủy tinh hóa học nằm ở cấu trúc áo khoác.
Một lò phản ứng thủy tinh có áo khoác bao gồm:
Môi trường gia nhiệt—chẳng hạn như nước, dầu silicon hoặc glycol—chảy đều xung quanh bình bên trong, truyền nhiệt gián tiếp qua thành thủy tinh borosilicate. Phương pháp gia nhiệt gián tiếp này đảm bảo phân bố nhiệt độ đồng đều mà không có sự tiếp xúc trực tiếp giữa nguồn nhiệt và vật liệu phản ứng.
Bộ Phận Kiểm Soát Nhiệt Độ và Hệ Thống Tuần Hoàn
Lò phản ứng thủy tinh hóa học thường được kết nối với các bộ phận kiểm soát nhiệt độ bên ngoài. Các hệ thống này cho phép người vận hành:
Đặt nhiệt độ mục tiêu chính xác
Điều chỉnh tốc độ gia nhiệt và làm mát
Duy trì điều kiện ổn định trong thời gian phản ứng dài
Bơm tuần hoàn chất lượng cao đảm bảo dòng chảy liên tục của môi trường gia nhiệt, giảm thiểu gradient nhiệt độ và ngăn ngừa quá nhiệt hoặc làm mát cục bộ.
Ưu Điểm của Thủy Tinh Borosilicate để Truyền Nhiệt
Thủy tinh Borosilicate đóng một vai trò quan trọng trong việc ổn định nhiệt độ. Các đặc tính của nó bao gồm:
Khả năng chống sốc nhiệt tuyệt vời
Hiệu suất ổn định trong phạm vi nhiệt độ rộng
Đặc tính truyền nhiệt nhất quán
Những tính năng này cho phép lò phản ứng thủy tinh hóa học xử lý cả quá trình gia nhiệt và làm mát nhanh chóng mà không ảnh hưởng đến an toàn hoặc hiệu suất.
Tầm Quan Trọng của Khuấy và Trộn
Kiểm soát nhiệt độ chính xác không chỉ là về gia nhiệt hoặc làm mát—nó còn phụ thuộc vào việc trộn hiệu quả. Lò phản ứng thủy tinh hóa học được trang bị hệ thống khuấy cơ học giúp:
Phân phối nhiệt đều khắp hỗn hợp phản ứng
Ngăn chặn các điểm nóng hoặc vùng lạnh
Cải thiện hiệu quả và tính nhất quán của phản ứng
Khuấy trộn thích hợp đảm bảo rằng tất cả các chất phản ứng đều trải qua các điều kiện nhiệt tương tự, điều này rất quan trọng để có được kết quả có thể tái tạo.
Vận Hành Chân Không và Kiểm Soát Nhiệt Độ
Nhiều lò phản ứng thủy tinh hóa học hỗ trợ vận hành chân không, giúp tăng cường hơn nữa khả năng kiểm soát nhiệt độ. Trong điều kiện chân không:
Điểm sôi của dung môi giảm
Phản ứng có thể xảy ra ở nhiệt độ thấp hơn
Sự suy thoái nhiệt của các vật liệu nhạy cảm được giảm thiểu
Khả năng này đặc biệt có giá trị trong các ứng dụng dược phẩm và hóa chất tốt.
Các Thách Thức và Giải Pháp Kiểm Soát Nhiệt Độ Phổ Biến
| Thách Thức |
Cách Lò Phản Ứng Thủy Tinh Giải Quyết Vấn Đề |
| Gia nhiệt không đều |
Thiết kế áo khoác đảm bảo truyền nhiệt đồng đều |
| Vượt quá nhiệt độ |
Bộ điều khiển bên ngoài cung cấp khả năng điều chỉnh chính xác |
| Phản ứng không ổn định |
Môi trường nhiệt ổn định cải thiện khả năng kiểm soát |
| Rủi ro về an toàn |
Gia nhiệt gián tiếp làm giảm nguy cơ quá nhiệt |
Kết Luận
Lò phản ứng thủy tinh hóa học đạt được khả năng kiểm soát nhiệt độ chính xác thông qua cấu trúc áo khoác, hệ thống tuần hoàn bên ngoài, thủy tinh borosilicate chất lượng cao và cơ chế khuấy trộn hiệu quả. Cùng nhau, những tính năng này tạo ra một môi trường phản ứng ổn định và có thể dự đoán được.
Đối với các phòng thí nghiệm và nhà máy thí điểm, nơi độ chính xác và an toàn là điều cần thiết, việc đầu tư vào một lò phản ứng thủy tinh hóa học hiệu suất cao là một quyết định thông minh.